| A: Two times | C: Three times | C: Ten times | D: Five times |
Introduction
Why Understanding Stopping Distances Matters
When driving in adverse conditions, understanding how stopping distances change is crucial for safety. Stopping distance is the total distance a vehicle travels from the moment the driver perceives a hazard to the point where the vehicle comes to a complete stop. This distance includes reaction time and braking distance. In normal conditions, this might be manageable, but in icy conditions, stopping distances can increase significantly, leading to higher chances of accidents if drivers aren’t prepared.
Impact of Weather Conditions on Driving
Weather conditions profoundly affect driving dynamics. Rain, snow, and ice alter the road surface, reducing tire traction and increasing stopping distances. Ice, in particular, creates a dangerously slippery surface that can make even the most straightforward driving maneuvers challenging. Understanding these effects helps drivers make better decisions, plan for longer stopping distances, and adapt their driving behavior to ensure safety.
How Many Times Can Stopping Distance Increase in Icy Conditions?
General Increase in Stopping Distance
In icy conditions, stopping distances can increase dramatically compared to normal conditions. On a dry road, a car might take about 40-60 meters to stop from a speed of 50 km/h. However, on ice, this distance can be significantly longer due to the lack of friction between the tires and the road surface.
Specific Figures: Up to Ten Times
Research and real-world driving tests reveal that stopping distances on ice can increase up to ten times compared to dry conditions. This means that if you normally require 50 meters to stop, you might need up to 500 meters on an icy surface. This exponential increase underscores the critical importance of adjusting your driving habits in icy conditions to prevent accidents.
What is the Stopping Distance on an Icy Road?
Definition of Stopping Distance
Stopping distance is the sum of the reaction distance and the braking distance. Reaction distance is the distance a car travels while the driver is reacting to a hazard, and braking distance is the distance the car travels while braking to a stop. On icy roads, both components are affected, leading to a much longer stopping distance.
Average Stopping Distance in Icy Conditions
On an icy road, the average stopping distance can be vastly different from that on a dry surface. For example, at 30 km/h, the stopping distance on ice might exceed 100 meters, compared to just 20-30 meters on a dry road. This dramatic increase highlights the critical need for drivers to slow down and maintain greater following distances in icy conditions.
Factors Affecting Stopping Distance
Several factors influence stopping distance on icy roads, including the thickness of the ice, the type of tires used, and the vehicle’s weight. Thin ice might offer slightly more traction than thick, compacted ice. Additionally, winter tires with specialized treads provide better grip, reducing stopping distances compared to standard tires. Vehicle weight also plays a role; heavier vehicles may take longer to stop due to increased momentum.
How Much is the Stopping Distance in Ice?
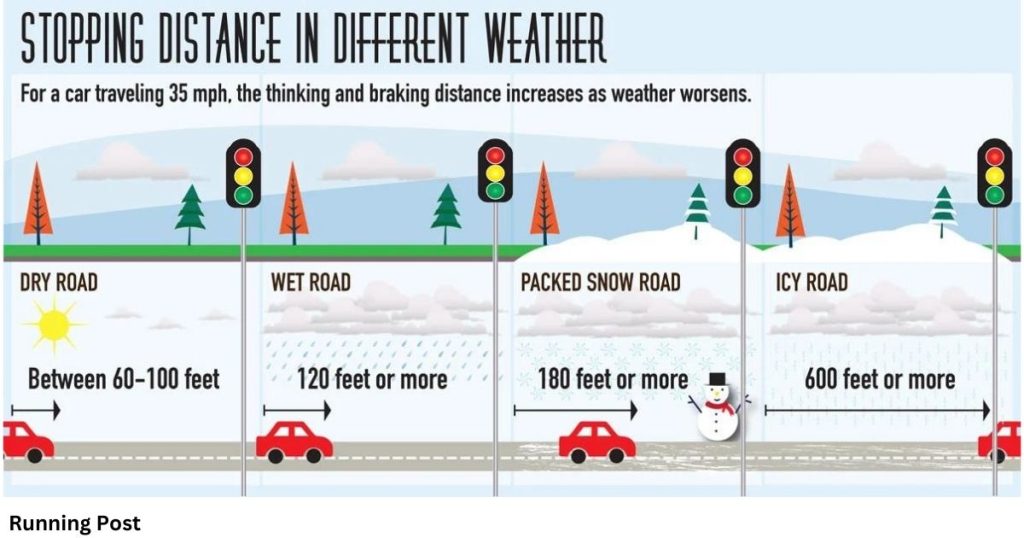
Comparison with Normal Conditions
In normal driving conditions, a vehicle’s stopping distance is relatively predictable based on speed and road conditions. However, on ice, this distance can be vastly longer. For instance, where you might comfortably stop within 50 meters on a dry road, you might need up to 500 meters on ice, illustrating the need for major adjustments in driving behavior.
Real-World Examples and Data
Data from various studies and driving tests show that stopping distances can vary greatly depending on the severity of ice and other factors. For example, tests conducted in controlled environments have shown that a vehicle traveling at 50 km/h on ice may require as much as ten times the stopping distance compared to a dry road. Real-world examples include numerous accidents during icy conditions where drivers underestimated the required stopping distance.
Influence of Vehicle Type and Speed
Different vehicles respond differently to icy conditions. For instance, heavier trucks might experience longer stopping distances due to their mass and the reduced traction of their tires. Conversely, lighter vehicles might have slightly shorter stopping distances but still require substantial increases compared to dry conditions. Speed is a major factor; higher speeds exponentially increase stopping distances, making slow driving essential on icy roads.
You Also Like It:
Which vehicle will use a blue flashing beacon?
What shape is a ‘give way’ sign?
Why are place names painted on the road surface?
How Much Should You Expect Stopping Distances to Increase in Freezing Conditions?
Percentage Increase in Stopping Distance
Stopping distances can increase by a significant percentage in freezing conditions. For example, if the stopping distance is normally 30 meters on a dry road, it could extend to 300 meters or more on ice. This increase underscores the need for drivers to be highly cautious and proactive in adjusting their driving speed and distance from other vehicles.
Impact of Freezing Rain vs. Snow
Freezing rain and snow each impact stopping distances differently. Freezing rain often creates a slick, smooth layer of ice, resulting in extremely long stopping distances. Snow, while still reducing traction, can sometimes provide slightly better grip than ice, though it still requires drivers to increase their stopping distances significantly compared to dry conditions.
Precautionary Measures for Drivers
To mitigate the increased risk of accidents due to longer stopping distances, drivers should take several precautionary measures. This includes reducing speed, increasing following distances, and avoiding sudden maneuvers. Additionally, ensuring your vehicle is equipped with appropriate winter tires can help improve traction and reduce stopping distances.
Tips for Safe Driving in Icy Conditions
Adjusting Your Speed
One of the most effective ways to drive safely in icy conditions is to adjust your speed. Lowering your speed gives you more time to react and increases the likelihood of stopping in time. It’s essential to drive at a speed that allows you to maintain control of your vehicle and stop safely if necessary.
Maintaining Safe Following Distances
Maintaining a greater following distance in icy conditions is crucial. This extra space provides ample time for you to stop if the vehicle in front of you brakes suddenly. On icy roads, increasing your following distance by at least three times the normal distance is a good rule of thumb.
Proper Use of Winter Tires
Winter tires are designed to provide better traction on ice and snow compared to all-season or summer tires. These tires have specialized treads that help grip the road and reduce stopping distances. Ensuring your vehicle is fitted with high-quality winter tires can significantly improve safety in icy conditions.
Conclusion About By how much can stopping distances increase in icy conditions?
Summary of Key Points
In summary, understanding the dramatic increase in stopping distances on icy roads is essential for safe driving. Stopping distances can increase up to ten times compared to dry conditions, and factors like ice thickness, vehicle type, and speed all play a role. By adjusting speed, maintaining safe following distances, and using winter tires, drivers can better navigate icy conditions.
Final Safety Recommendations
To stay safe in icy conditions, always drive cautiously and anticipate longer stopping distances. Regularly check your vehicle’s tires and ensure they are suitable for winter driving. By taking these precautions, you can help prevent accidents and ensure safer travel in challenging weather conditions.
You Also Like It:
In which THREE of these situations may you overtake another vehicle on the left?
What will help you to keep your car secure?
What does the white line along the side of the road indicate?
Releated Posts
MAB Instructor Certification: Your Gateway to Professional Crisis Management Leadership
In today’s fast-evolving professional environments—especially in healthcare, mental health, education, and corrections—conflict and aggression can arise without warning.…
Freewayget.com: Your Ultimate Platform for Deals, Discounts, and Digital Products
Introduction to Freewayget.com In today’s fast-paced digital world, finding reliable platforms that offer authentic discounts, deals, and digital…
Affordable & Fast Embroidery Digitizing Services in Your Area
Embroidery digitizing services provide corporations, designers, and people with brilliant embroidery-equipped designs by means of changing art work…
Introduction to hdhub4u nit
In this article, we will delve into the details of hdhub4u nit, exploring its features, benefits, and why…