Introduction
The question of whether “can tonsils grow back after being removed? – tymoff” is one that many people ponder after undergoing a tonsillectomy. Tonsils, small glands located at the back of the throat, play a role in the body’s immune system, particularly in young children. However, they can sometimes cause health issues, leading to their surgical removal. This article delves into the nature of tonsils, the reasons they are often removed, and the possibility and implications of their regrowth.
What Are Tonsils?
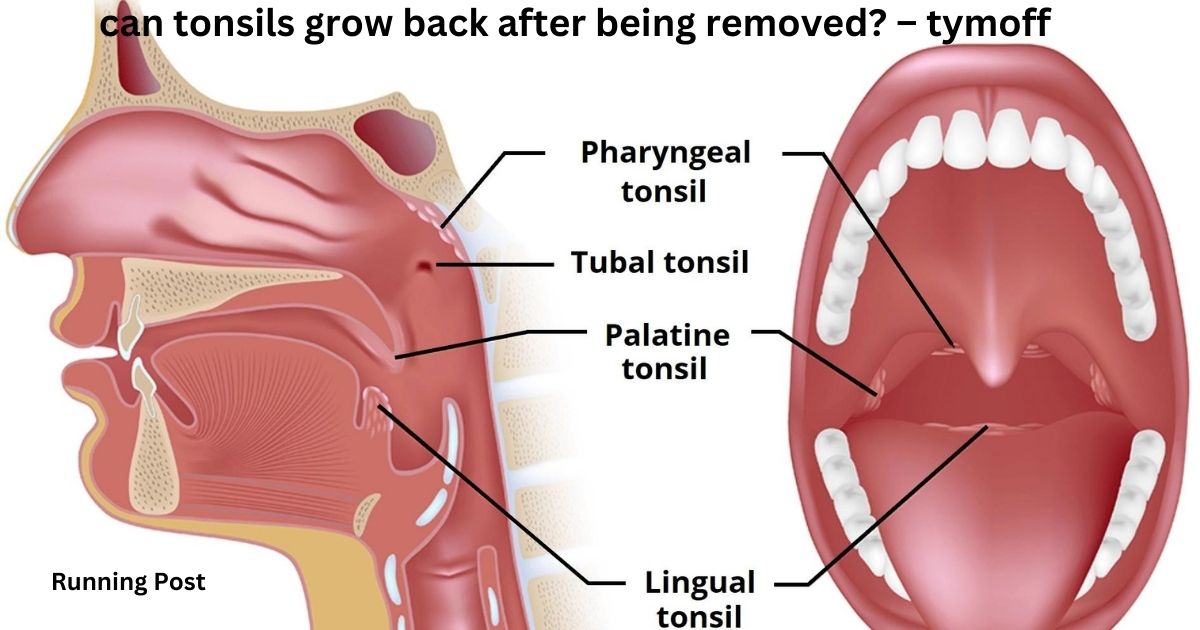
Tonsils are part of the lymphatic system, which helps the body fight infection. There are three types of tonsils: palatine tonsils, located on either side of the throat; pharyngeal tonsils, also known as adenoids, located in the roof of the nasopharynx; and lingual tonsils, located at the base of the tongue. These lymphoid tissues act as the first line of defense against pathogens entering through the mouth and nose, producing antibodies and trapping bacteria and viruses.
Types of Tonsils
There are three main types of tonsils in the human body:
1. Palatine Tonsils
- Location: Located at the back of the throat on both sides, these are the most commonly referenced tonsils when people talk about having their tonsils removed.
- Function: Palatine tonsils help trap and fight off bacteria and viruses that enter through the mouth and nose. They play a crucial role in the immune system, particularly during childhood.
2. Lingual Tonsils
- Location: Found at the base of the tongue, near the throat.
- Function: Lingual tonsils also serve to protect against infections, though they are less commonly removed compared to palatine tonsils.
3. Pharyngeal Tonsils (Adenoids)
- Location: Located high in the throat behind the nose, in the roof of the nasopharynx.
- Function: Pharyngeal tonsils, commonly known as adenoids, play a role in immune defense, particularly in children. They are part of the lymphatic system and help protect against infections entering through the nose.
Reasons for Tonsil Removal
Tonsil removal, or tonsillectomy, is a common procedure often recommended for recurrent tonsillitis, chronic tonsillitis, or sleep apnea caused by enlarged tonsils. Recurrent tonsillitis involves multiple episodes of sore throat and infection, while chronic tonsillitis refers to a long-lasting sore throat and swollen tonsils. Sleep apnea caused by enlarged tonsils can lead to breathing difficulties during sleep. Other reasons for tonsil removal include peritonsillar abscess, which is a collection of pus around the tonsils, and suspicion of tonsillar cancer.
The Possibility of Tonsil Regrowth
Understanding Tonsil Regrowth
Tonsil regrowth is a phenomenon that occurs when tonsil tissue regenerates after a tonsillectomy. Although it is relatively rare, it can happen, especially in cases where the tonsils were not completely removed. Regrowth happens because some of the tonsil tissue remains after surgery, and under certain conditions, this residual tissue can regenerate.
How Common Is It?
The incidence of tonsil regrowth varies, but it is generally considered to be uncommon. Studies suggest that the likelihood of tonsils growing back is higher in younger children because their bodies are more capable of regeneration. However, even in children, the occurrence is not frequent, with estimates indicating that it happens in less than 5% of tonsillectomy cases.
Medical Explanation
Partial Tonsillectomy vs. Total Tonsillectomy
A partial tonsillectomy, also known as tonsillotomy, involves the removal of only part of the tonsils. This approach is often used to reduce the size of the tonsils to alleviate symptoms without completely removing them. On the other hand, a total tonsillectomy aims to remove all of the tonsil tissue. However, even in total tonsillectomy, some microscopic tissue might remain, which can potentially lead to regrowth.
Residual Tonsil Tissue
Residual tonsil tissue refers to the small amounts of tonsil tissue that remain after surgery. This tissue can be left behind intentionally in a partial tonsillectomy or unintentionally in a total tonsillectomy. This leftover tissue has the potential to regenerate, especially if the immune response triggers growth as part of the body’s healing process.
Regrowth Mechanism
The regrowth of tonsil tissue involves the regeneration of lymphoid tissue. This process is influenced by various factors, including the body’s natural healing mechanisms and immune response. When the remaining tonsil tissue encounters pathogens, it may begin to grow again in an effort to fight off infections, similar to its original function.
Factors Influencing Tonsil Regrowth

Age and Healing Factors
Age plays a significant role in the likelihood of tonsil regrowth. Younger patients, particularly children, have a higher regenerative capacity than adults. This is because children’s tissues are more active in cell reproduction and healing. Additionally, the body’s healing response after surgery can influence whether residual tonsil tissue will regrow.
Surgical Technique
The technique used during the tonsillectomy can also affect the likelihood of regrowth. Surgeons aim to remove as much of the tonsil tissue as possible, but in some cases, microscopic remnants may be left behind. The more meticulous the surgery, the lower the chances of regrowth. However, the balance between complete removal and minimizing damage to surrounding tissues is crucial.
Individual Variation
Each person’s body responds differently to surgery and healing. Factors such as genetics, overall health, and immune response can influence the potential for tonsil regrowth. Some individuals may have a stronger tendency for tissue regeneration, while others may not experience regrowth at all.
Symptoms of Tonsil Regrowth
Recognizing the Signs
If tonsils begin to regrow, symptoms can include a sore throat, difficulty swallowing, bad breath, and the reappearance of white or yellow patches on the tonsils. These symptoms can be similar to those experienced before the initial tonsillectomy, which can help in recognizing the regrowth.
When to Consult a Doctor
It’s essential to consult a doctor if you notice symptoms that may indicate tonsil regrowth. Persistent sore throat, difficulty swallowing, or other related symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. Early consultation can help in managing symptoms and deciding on the appropriate course of action.
You Also Like It:
Where Are Amber Reflective Studs Found on a Motorway
how i sleep at night knowing l’m failing all my cl – tymoff
Medical Opinions and Studies
Expert Views on Tonsil Regrowth
Medical experts generally agree that tonsil regrowth is rare but possible. Otolaryngologists, who specialize in ear, nose, and throat disorders, often emphasize the importance of complete removal during a tonsillectomy to minimize the chances of regrowth. However, they also acknowledge that in some cases, regrowth can occur despite meticulous surgical techniques.
Research Findings
Research on tonsil regrowth has shown varying results, but overall, the incidence is low. Studies have focused on identifying the factors that contribute to regrowth and the best surgical practices to prevent it. Findings suggest that younger patients and those undergoing partial tonsillectomy are more likely to experience regrowth.
Treatment Options for Regrown Tonsils
Non-Surgical Treatments
In cases of tonsil regrowth, non-surgical treatments may include medications to manage symptoms, such as pain relievers and antibiotics if an infection is present. Monitoring and regular check-ups can help manage the condition without immediate resort to surgery.
Surgical Interventions
If symptoms persist or cause significant discomfort, a second surgical intervention might be necessary. This could involve another tonsillectomy to remove the regrown tissue. The decision for additional surgery depends on the severity of symptoms and the impact on the patient’s quality of life.
Conclusion
Managing Expectations
Understanding that tonsil regrowth is rare but possible helps manage expectations post-surgery. Patients should be aware of the potential signs of regrowth and maintain regular follow-ups with their healthcare provider to ensure timely intervention if needed.
Final Thoughts
While the possibility of tonsil regrowth exists, it is relatively uncommon and typically manageable. Awareness and proper medical guidance are key to addressing any issues that may arise. Whether through monitoring or additional treatment, patients can effectively handle the situation and maintain their health.
FAQs about Can Tonsils Grow Back After Being Removed? – Tymoff
Can everyone’s tonsils grow back after being removed?
Not everyone experiences tonsil regrowth after a tonsillectomy. The likelihood of regrowth depends on various factors such as the surgical technique used, the amount of tissue removed, and individual healing responses. Complete regrowth of tonsils is rare, occurring in less than 1% of cases, but partial regrowth, where small amounts of tonsillar tissue reform, is more common.
Is tonsil regrowth harmful?
In most cases, tonsil regrowth is not harmful. However, it can lead to symptoms similar to those experienced before the tonsillectomy, such as recurrent sore throat, difficulty swallowing, or enlargement of the tonsils in the throat. If symptoms persist or worsen, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for evaluation and appropriate management.
What should I do if my tonsils grow back?
If you suspect your tonsils have regrown or if you experience symptoms suggestive of tonsil regrowth, such as persistent throat discomfort or difficulty breathing, it’s crucial to seek medical advice promptly. An ENT specialist can evaluate your condition, perform necessary tests, and recommend appropriate treatment options, which may include medication or, in severe cases, surgical intervention to address the regrown tissue.
How can I prevent tonsil regrowth after a tonsillectomy?
While complete prevention of tonsil regrowth may not be entirely possible, certain measures can help minimize the risk:
- Choose an experienced ENT surgeon who employs thorough surgical techniques to remove as much tonsil tissue as necessary.
- Follow post-operative care instructions diligently, including proper wound care and avoiding activities that may irritate the throat.
- Attend follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider to monitor healing progress and address any concerns promptly.
Are there any advancements in surgery to reduce the risk of tonsil regrowth?
Advancements in surgical techniques and technology have led to improved outcomes in tonsillectomy procedures. Techniques such as coblation and laser-assisted tonsillectomy aim to minimize tissue trauma and reduce the likelihood of residual tonsil tissue, thereby lowering the risk of regrowth. Consulting with a qualified ENT specialist can provide insights into the latest surgical options available.
What are the long-term implications of tonsil regrowth?
While the long-term implications of tonsil regrowth are generally manageable, persistent symptoms may require ongoing medical attention. Regular monitoring and prompt treatment of recurrent symptoms can help alleviate discomfort and improve overall quality of life. Working closely with healthcare providers ensures timely intervention and appropriate management of any complications related to tonsil regrowth.
You Also Like It:
It Is Not Wisdom But Authority That Makes A Law. T – Tymoff
how i sleep at night knowing l’m failing all my cl – tymoff