| A: 60 mph | B: 30 mph | C: 70 mph | D: 50 mph |
Understanding Dual Carriageways
Dual carriageways are a vital part of modern road networks, designed to manage heavy traffic while ensuring safety and efficiency. These roads are distinct from other types of carriageways due to their layout, features, and intended use. Understanding what a dual carriageway is and how it functions is essential for all road users, whether they are driving cars, motorcycles, or larger vehicles.
A dual carriageway typically consists of two separate roadways, each carrying traffic in opposite directions, separated by a central reservation. This design helps to minimize the risk of head-on collisions and allows for higher speed limits compared to single carriageways. The layout is especially beneficial in areas with high traffic volumes, providing a safer and more efficient means of travel.
The characteristics of a dual carriageway can vary depending on its location and the volume of traffic it is designed to handle. However, all dual carriageways share some common features, including multiple lanes, central reservations, and clear road markings that guide drivers and help maintain order on the road. These elements contribute to the overall safety and functionality of dual carriageways, making them a preferred choice for major routes in many countries.
What is a Dual Carriageway?
A dual carriageway is a road that has two separate carriageways, one for each direction of traffic. These carriageways are typically divided by a central reservation, which can be a simple barrier, a grassy median, or even a more substantial structure like a concrete wall. The primary purpose of a dual carriageway is to improve traffic flow and reduce the risk of accidents, particularly head-on collisions.
In contrast to single carriageways, where all traffic shares the same road surface, dual carriageways provide a distinct separation between opposing lanes of traffic. This separation not only enhances safety but also allows for higher speed limits, as vehicles are less likely to encounter oncoming traffic.
Dual carriageways are commonly found on major routes and highways, where traffic volumes are high, and the need for efficient, safe travel is paramount. They are often used in urban areas to connect cities and towns, as well as in rural areas where long-distance travel is common. The design of a dual carriageway can vary, with some roads featuring two lanes in each direction and others having more lanes to accommodate even heavier traffic.
What Does a Dual Carriageway Look Like?
A dual carriageway typically features two or more lanes in each direction, separated by a central reservation. This reservation can take various forms, from simple grass verges to more robust barriers designed to prevent vehicles from crossing into oncoming traffic. The lanes are usually marked with clear, painted lines, and the road surface is often of high quality to support higher speed limits.
One of the key visual differences between a dual carriageway and other types of roads is the presence of the central reservation. This physical separation is a defining characteristic of dual carriageways and plays a crucial role in enhancing safety. The central reservation not only prevents vehicles from crossing into the opposite lane but also helps to manage traffic flow by reducing the chances of head-on collisions.
In addition to the central reservation, dual carriageways often have features like slip roads for entering and exiting the road, as well as service areas for refueling and rest. The overall layout is designed to support high-speed travel, with gentle curves and wide lanes that accommodate a variety of vehicles, from motorcycles to large trucks.
National Speed Limits on Dual Carriageways
In the UK, dual carriageways are subject to specific national speed limits that vary depending on the type of vehicle. These speed limits are set to ensure the safety of all road users while allowing for efficient travel across the road network. Understanding these speed limits is crucial for drivers to avoid penalties and contribute to safer roads.
What’s the National Speed Limit for Cars and Motorcycles on a Dual Carriageway?
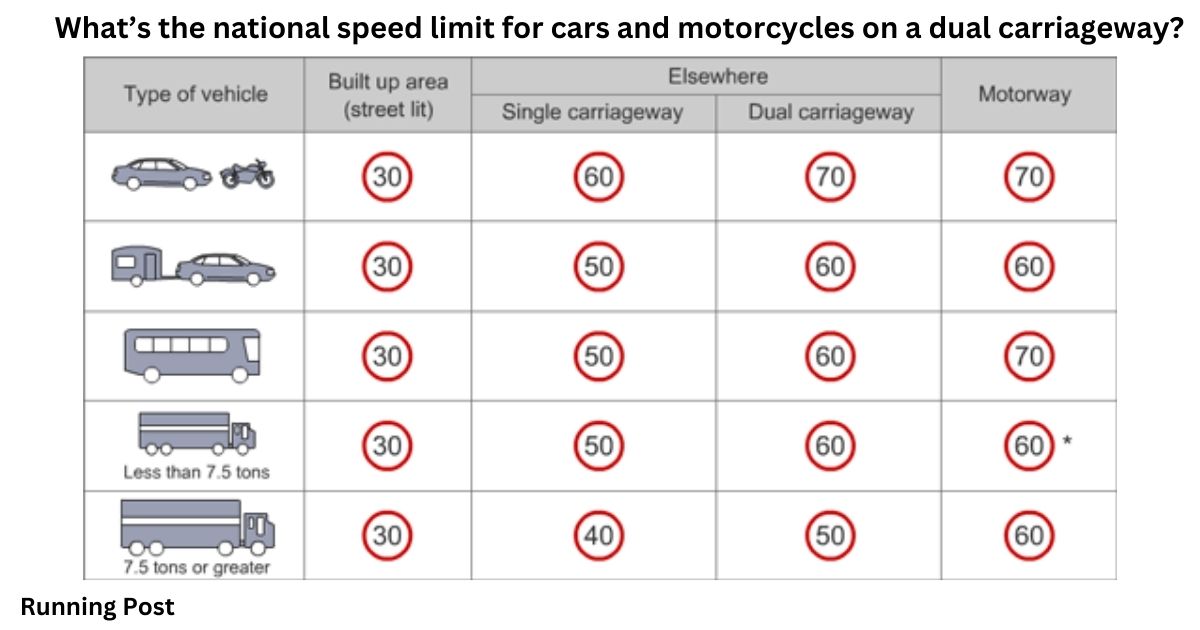
The national speed limit for cars and motorcycles on a dual carriageway in the UK is 70 mph. This speed limit is in place to ensure that vehicles can travel at a pace that is both efficient and safe, taking into account the design of the road and the volume of traffic. The 70 mph limit allows drivers to cover long distances quickly while maintaining control of their vehicles.
Adhering to the 70 mph speed limit is not only a legal requirement but also a key factor in ensuring road safety. Driving at higher speeds increases the risk of accidents, particularly in situations where drivers may need to react quickly to changes in traffic conditions. By keeping within the speed limit, drivers can reduce the likelihood of collisions and contribute to the overall safety of the road network.
What’s the National Speed Limit for Cars and Motorcycles on a Motorway in the UK?
On UK motorways, which are designed for even higher-speed travel than dual carriageways, the national speed limit for cars and motorcycles is also 70 mph. While this might seem identical to the dual carriageway limit, motorways typically have more lanes, fewer junctions, and additional safety features that support high-speed travel. This makes motorways safer at this speed compared to dual carriageways.
However, certain conditions may warrant a reduction in speed, such as adverse weather, roadworks, or heavy traffic. In these cases, variable speed limits may be implemented, and drivers are legally required to adhere to them. Understanding the difference between motorways and dual carriageways in terms of speed limits and road features is essential for safe driving.
Differences Between Carriageways
The UK road network includes various types of carriageways, each with its own characteristics and speed limits. The primary difference between a single carriageway and a dual carriageway lies in their design and the level of separation between opposing lanes of traffic.
What is the Difference Between a Single Carriageway and a Dual Carriageway?
A single carriageway is a road where traffic in both directions shares the same road surface, with no central reservation to separate opposing lanes. This layout typically means lower speed limits and a higher risk of head-on collisions, as vehicles are traveling in close proximity to one another. Single carriageways are common in rural areas and on smaller roads where traffic volumes are lower.
In contrast, a dual carriageway features a central reservation that physically separates the two directions of traffic. This design reduces the risk of head-on collisions and allows for higher speed limits, typically 70 mph in the UK. Dual carriageways are often used on major routes where traffic volumes are high, and safety is a priority.
You also Like It:
How much more fuel will you use by driving at 70 mph, compared with driving at 50 mph?
What Should you do Immediately After Joining a Motorway?
What should you do before driving into a tunnel?
Speed Limits on Single vs. Dual Carriageways
Speed limits on single and dual carriageways vary significantly due to their design differences. On a single carriageway, the national speed limit for cars and motorcycles is 60 mph, which is lower than the 70 mph limit on dual carriageways. This lower limit reflects the increased risk associated with the lack of a central reservation and the closer proximity of opposing traffic.
The higher speed limit on dual carriageways is possible because the road design reduces the risk of collisions and supports higher-speed travel. However, drivers must still be cautious and adjust their speed according to road conditions, traffic volume, and weather. Legal implications for exceeding the speed limit on either type of carriageway can include fines, points on your driving license, and even disqualification.
Regional Speed Limits
Speed limits can vary significantly from one region to another, particularly between countries. In the United States, for example, speed limits are set by individual states and can differ from those in the UK. Understanding these regional differences is crucial for drivers who travel internationally or within different regions of a country.
What is the Maximum Speed Limit for Cars and Trucks on a Two-Lane Highway in Mississippi?

In Mississippi, the maximum speed limit for cars on a two-lane highway is generally 65 mph, though this can vary depending on the specific road and location. Trucks, particularly those weighing over 10,000 pounds, may be subject to lower speed limits to account for their longer stopping distances and potential safety risks.
This speed limit is lower than the UK’s dual carriageway limit of 70 mph, reflecting differences in road design, traffic volumes, and safety standards between the two regions. Drivers in Mississippi must be aware of these limits and adjust their speed accordingly to ensure safe travel.
Motorcycle Speed Limits in the UK
Motorcycles are subject to the same speed limits as cars on most UK roads, including dual carriageways and motorways. However, motorcyclists must also consider additional factors, such as road conditions and their own safety, when choosing their speed.
What is the Motorcycle Speed Limit in the UK?
The speed limit for motorcycles on a dual carriageway in the UK is 70 mph, the same as for cars. This limit applies regardless of the size or power of the motorcycle, though riders are advised to adjust their speed based on road conditions, traffic, and their own skill level.
Motorcyclists should be particularly cautious when riding at higher speeds, as they are more vulnerable in the event of an accident compared to car drivers. Proper safety gear, including helmets, gloves, and protective clothing, is essential for reducing the risk of injury in a crash.
Safe Driving Practices on Dual Carriageways
Driving on a dual carriageway requires awareness, attention, and adherence to speed limits to ensure safety for all road users. By following best practices and being prepared for emergencies, drivers can navigate these roads safely and efficiently.
Tips for Safe Driving on a Dual Carriageway
Driving on a dual carriageway can be smooth and efficient if done correctly. These roads are designed for higher speeds and heavy traffic, making it crucial to follow safe driving practices. Here are some essential tips to ensure safety while driving on a dual carriageway:
Maintain a Safe Speed
One of the most important tips for safe driving on a dual carriageway is to adhere to the speed limit, which is typically 70 mph in the UK. While this speed limit allows for faster travel, it’s essential to adjust your speed based on current road conditions. For example, if the weather is poor, such as during rain, fog, or icy conditions, reducing your speed is critical to maintain control of your vehicle. Remember that the speed limit is a maximum, not a target.
Keep a Safe Following Distance
Maintaining a safe following distance from the vehicle in front of you is crucial, especially at higher speeds. A general rule of thumb is to keep at least a two-second gap between your car and the vehicle ahead in normal conditions. In adverse weather, this gap should be increased to account for longer stopping distances. This buffer zone allows you more time to react if the vehicle in front of you suddenly brakes or encounters an obstacle.
Use Your Mirrors Frequently
On a dual carriageway, it’s important to be aware of other vehicles around you, including those in adjacent lanes and those approaching from behind. Regularly check your mirrors to monitor the traffic situation and be aware of vehicles that may be overtaking or merging into your lane. This awareness helps in making informed decisions, whether you’re changing lanes or adjusting your speed.
Signal Your Intentions Clearly
Always use your indicators to signal your intentions when changing lanes or exiting the dual carriageway. Signaling early and clearly gives other drivers time to adjust their speed or position, reducing the risk of collisions. It’s particularly important to signal well in advance when moving from a faster lane to a slower lane, as other vehicles may be traveling at high speeds.
Be Aware of Slip Roads
Slip roads are used for entering and exiting dual carriageways. When joining the dual carriageway from a slip road, ensure you match your speed to the flow of traffic and merge safely into the appropriate lane. Similarly, when exiting, signal early and move into the deceleration lane in good time. Avoid cutting across lanes at the last minute, as this can cause confusion and accidents.
Stay in the Appropriate Lane
On dual carriageways, the left lane is for normal driving, while the right lane is generally used for overtaking. After overtaking, it’s important to return to the left lane to allow faster-moving traffic to pass. Hogging the right lane can lead to congestion and frustration among other drivers, increasing the likelihood of dangerous driving behavior.
Be Mindful of Large Vehicles
Large vehicles like trucks and buses have longer stopping distances and may have blind spots that can obscure smaller vehicles. When overtaking these vehicles, do so quickly and safely, ensuring that you have enough space to move back into the left lane once you’ve passed them. Avoid staying in a large vehicle’s blind spot, as the driver may not see you when changing lanes or adjusting their position.
Prepare for Emergencies
Even with the best driving practices, emergencies can happen. If your vehicle breaks down on a dual carriageway, pull over to the hard shoulder or a safe area as soon as possible. Turn on your hazard lights to alert other drivers, and if it’s safe, exit the vehicle and stand behind the safety barrier. Having a roadside emergency kit, including a reflective jacket, warning triangle, and basic tools, can be extremely helpful in these situations.
By following these tips, you can drive more safely and confidently on dual carriageways, reducing the risk of accidents and ensuring a smoother journey for yourself and others on the road.
What to Do in Case of an Emergency on a Dual Carriageway
If your vehicle breaks down or you encounter an emergency on a dual carriageway, it’s important to remain calm and take immediate steps to ensure your safety. Pull over to the hard shoulder or a safe area if possible, and turn on your hazard lights to alert other drivers.
It’s also advisable to exit your vehicle and stand behind the safety barrier if one is available, especially if you are on the side of the road where traffic is moving quickly. Keeping a safety kit in your car, including items like a reflective jacket, warning triangle, and first aid supplies, can be invaluable in these situations.
You Also Like It:
You’re driving a car fitted with automatic transmission. Why would you use kick-down?
Releated Posts
MAB Instructor Certification: Your Gateway to Professional Crisis Management Leadership
In today’s fast-evolving professional environments—especially in healthcare, mental health, education, and corrections—conflict and aggression can arise without warning.…
Freewayget.com: Your Ultimate Platform for Deals, Discounts, and Digital Products
Introduction to Freewayget.com In today’s fast-paced digital world, finding reliable platforms that offer authentic discounts, deals, and digital…
Affordable & Fast Embroidery Digitizing Services in Your Area
Embroidery digitizing services provide corporations, designers, and people with brilliant embroidery-equipped designs by means of changing art work…
Introduction to hdhub4u nit
In this article, we will delve into the details of hdhub4u nit, exploring its features, benefits, and why…