| A: o Cool Down Exhaust Gases | B: To reduce harmful exhaust gases | C: To Improve Fuel Efficiency | D: To reduce engine wear |
Introduction
Catalytic converters are an integral part of modern automotive technology, designed to tackle the pressing issue of vehicle emissions. They are a critical component of the exhaust system, working quietly but efficiently to reduce the environmental impact of harmful gases produced by internal combustion engines. The importance of catalytic converters cannot be overstated, as they play a pivotal role in meeting emissions regulations and improving air quality. This article aims to explore the multifaceted purpose of catalytic converters, including their primary function, the related theory test, the role of catalysts in these converters, and the broader benefits they provide. Understanding how catalytic converters work and their significance helps vehicle owners maintain their cars better, comply with environmental laws, and contribute to a healthier planet. By examining each aspect in detail, we can appreciate the technology behind catalytic converters and its crucial role in reducing pollution and enhancing vehicle performance.
- Catalytic converters are essential for minimizing vehicle emissions.
- They play a key role in environmental protection and vehicle performance.
- A thorough understanding of their function is crucial for vehicle maintenance and regulatory compliance.
What is the Main Purpose of a Catalytic Converter?
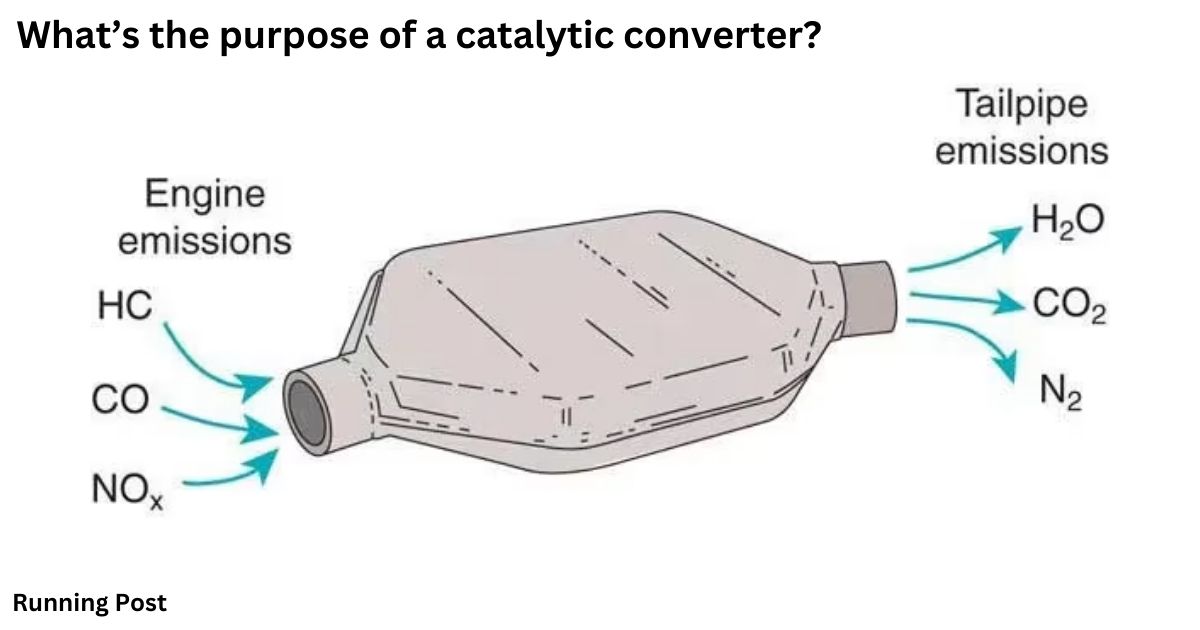
The main purpose of a catalytic converter is to significantly reduce the harmful emissions that result from the combustion process in a vehicle’s engine. These converters are designed to transform three major pollutants—carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides—into less harmful substances before they are released into the atmosphere. Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless gas that is highly toxic and results from incomplete combustion of fuel. Hydrocarbons (HC) are unburned fuel particles that contribute to smog formation and air pollution. Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are gases that contribute to acid rain and respiratory problems. The catalytic converter uses a catalyst, often made from precious metals like platinum, palladium, and rhodium, to facilitate chemical reactions that convert these pollutants into:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2): A gas that is a natural part of the environment and less harmful compared to carbon monoxide.
- Nitrogen (N2): An inert gas that does not contribute to pollution.
- Water vapor (H2O): A harmless byproduct of the chemical reactions.
These reactions occur within the catalytic converter’s substrate, which provides a surface for the catalyst to work effectively. By converting these harmful gases into less damaging emissions, catalytic converters help reduce air pollution and contribute to cleaner, healthier environments. Their efficiency in this process is vital for meeting environmental regulations and improving overall air quality.
- Catalytic converters significantly reduce the amount of harmful emissions.
- They convert toxic gases into less harmful substances.
- This process helps improve air quality and complies with environmental standards.
What is the Purpose of a Catalytic Converter Theory Test?
The catalytic converter theory test is designed to ensure that individuals understand the principles and importance of catalytic converters in vehicle emissions control. This test is a crucial part of vehicle maintenance and regulatory compliance, as it assesses an individual’s knowledge about how these components function and their role in reducing emissions. The test covers various aspects, including the operation of catalytic converters, their significance in reducing pollution, and the regulatory requirements related to emissions. By passing this test, individuals demonstrate their understanding of how to maintain and monitor catalytic converters to ensure they are functioning properly.
Understanding the Theory Test
The theory test evaluates:
- Knowledge of how catalytic converters operate: It checks whether individuals understand the chemical reactions involved and how these reactions help in reducing harmful emissions.
- Awareness of emissions regulations: The test ensures that individuals are familiar with the legal standards for vehicle emissions and the role of catalytic converters in meeting these standards.
The theory test is important because:
- It ensures that vehicle owners and mechanics are knowledgeable about emissions control: Proper knowledge helps in maintaining vehicles in compliance with environmental regulations.
- It helps prevent emissions-related issues: Understanding the principles behind catalytic converters can aid in early detection of problems and ensure timely maintenance.
- The theory test is crucial for ensuring proper maintenance and compliance.
- It assesses understanding of catalytic converter operation and emissions regulations.
- Passing the test helps prevent emissions-related issues and ensures regulatory compliance.
Objectives of the Theory Test
The primary objectives of the theory test are to:
- Test knowledge of catalytic converters and their maintenance: Ensure that individuals understand how these components work and how to keep them functioning effectively.
- Assess understanding of emissions regulations: Evaluate familiarity with legal requirements and the role of catalytic converters in adhering to these standards.
The theory test is designed to:
- Ensure that individuals can properly maintain catalytic converters: Knowledge of their function and importance helps in effective vehicle maintenance.
- Promote compliance with emissions standards: Proper understanding contributes to meeting regulatory requirements and reducing environmental impact.
- The test evaluates knowledge of catalytic converter maintenance and emissions regulations.
- It ensures compliance with emissions standards and proper vehicle maintenance.
- Understanding these concepts helps in reducing environmental impact.
Importance in Vehicle Maintenance and Emissions Control
The theory test is crucial for several reasons:
- Ensures proper maintenance: Understanding the principles of catalytic converters helps vehicle owners and mechanics perform necessary maintenance tasks to keep the system working efficiently.
- Helps in regulatory compliance: Knowledge of emissions control and regulatory standards ensures that vehicles meet legal requirements, avoiding fines and contributing to cleaner air.
For vehicle owners:
- Proper maintenance of catalytic converters helps in reducing emissions and improving vehicle performance.
- Compliance with emissions regulations is essential for avoiding legal issues and contributing to environmental protection.
- The theory test ensures proper maintenance and regulatory compliance.
- It helps vehicle owners avoid fines and contribute to cleaner air.
- Understanding emissions control is crucial for effective vehicle maintenance.
How the Theory Test Relates to Catalytic Converters

The theory test relates directly to catalytic converters by:
- Evaluating understanding of how these components function: It tests knowledge of the chemical reactions that occur within catalytic converters and their role in emissions reduction.
- Assessing the impact of well-maintained catalytic converters: Proper knowledge helps ensure that these components operate effectively, contributing to overall vehicle performance and environmental health.
The test covers:
- Principles of catalytic converter operation: Understanding how these devices work helps in effective maintenance and monitoring.
- Regulatory implications: Familiarity with emissions standards ensures compliance and reduces environmental impact.
- The test evaluates understanding of catalytic converter function and maintenance.
- It assesses the impact of well-maintained converters on vehicle performance and emissions.
- Understanding these principles contributes to regulatory compliance and environmental protection.
Knowledge Areas Covered
The theory test covers several key areas, including:
- Function and structure of catalytic converters: Understanding how these components work and their role in emissions control.
- Regulatory standards for emissions: Knowledge of legal requirements and how catalytic converters help meet these standards.
These areas are essential for:
- Ensuring proper maintenance and operation of catalytic converters: Knowledge of their function and regulatory requirements helps in maintaining these components effectively.
- Contributing to environmental protection and regulatory compliance: Proper understanding supports meeting legal standards and reducing pollution.
- The test covers catalytic converter function, structure, and regulatory standards.
- Knowledge of these areas is essential for maintenance and compliance.
- Understanding contributes to environmental protection and regulatory adherence.
Practical Implications for Vehicle Owners
For vehicle owners, understanding catalytic converters and their maintenance has several practical implications:
- Improves vehicle performance: Proper maintenance ensures that catalytic converters work efficiently, which can enhance overall vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
- Reduces the risk of fines and penalties: Compliance with emissions regulations helps avoid legal issues and associated costs.
Understanding these concepts helps vehicle owners:
- Maintain their vehicles effectively: Knowledge of catalytic converters and emissions control supports proper maintenance and operation.
- Ensure regulatory compliance: Meeting emissions standards contributes to environmental protection and avoids legal problems.
- Understanding catalytic converters improves vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
- It helps in avoiding fines and ensures regulatory compliance.
- Knowledge supports effective maintenance and environmental protection.
You Also Like It:
Why are these yellow lines painted across the road?
how should you use the lanes on a motorway?
What does it mean when there are double red lines running along the edge of a road?
What is the Purpose of a Catalyst?
A catalyst is a substance that accelerates a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. In catalytic converters, catalysts are essential for facilitating the chemical reactions needed to reduce harmful emissions. They work by providing a surface that allows reactants to interact more efficiently, thus speeding up the reaction rate. Catalysts are crucial in converting toxic exhaust gases into less harmful substances, helping to meet environmental standards and improve air quality.
Definition of a Catalyst
- A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction: It does so by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur.
- It remains unchanged after the reaction: This allows it to be used repeatedly in multiple reactions without being depleted.
Catalysts are used in various chemical processes, including those in catalytic converters, to improve reaction efficiency and reduce the energy needed for the reactions to take place.
- Catalysts accelerate reactions by lowering activation energy.
- They remain unchanged and can be used repeatedly.
- They are crucial in various chemical processes, including emissions reduction.
Basic Chemistry Behind Catalysts
Catalysts work by:
- Providing an alternative reaction pathway: This pathway requires less energy for the reaction to proceed.
- Offering a surface for reactants to interact: The surface of the catalyst allows reactants to come into contact more effectively, speeding up the reaction.
In catalytic converters:
- The catalyst facilitates the conversion of harmful gases into less harmful substances.
- It enables these reactions to occur at lower temperatures, improving efficiency.
Understanding the basic chemistry behind catalysts helps in appreciating their role in catalytic converters and their importance in emissions control.
- Catalysts provide an alternative reaction pathway and lower activation energy.
- They facilitate efficient reactions in catalytic converters.
- Understanding this chemistry highlights their importance in emissions control.
Role of Catalysts in Catalytic Converters
In catalytic converters, catalysts play a crucial role by:
- Facilitating chemical reactions that convert harmful gases: Catalysts help in transforming carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides into less harmful substances.
- Enabling reactions to occur at lower temperatures: This improves the efficiency of the catalytic converter and ensures effective emissions reduction.
The use of catalysts in catalytic converters:
- Ensures that the exhaust gases are treated before being released into the atmosphere.
- Helps meet environmental regulations and reduce the vehicle’s impact on air quality.
- Catalysts facilitate the conversion of harmful gases into less harmful substances.
- They enable reactions to occur at lower temperatures for improved efficiency.
- Their role is crucial in meeting environmental standards and reducing pollution.
Specific Functions in Exhaust Gas Reduction
Catalysts in catalytic converters have specific functions in reducing exhaust gases:
- Carbon monoxide (CO) is converted into carbon dioxide (CO2): This transformation reduces the toxicity of the exhaust gases.
- Hydrocarbons (HC) are converted into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O): This helps in reducing smog and air pollution.
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are reduced to nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2): This process helps in minimizing the formation of acid rain and improving air quality.
These functions are essential for:
- Reducing the environmental impact of vehicle emissions.
- Ensuring that vehicles comply with emissions regulations and contribute to cleaner air.
- Catalysts convert carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides into less harmful substances.
- They help reduce the environmental impact and meet regulatory standards.
- Their functions are essential for improving air quality and reducing pollution.
Types of Catalysts Used
In catalytic converters, various types of catalysts are used to facilitate the necessary chemical reactions:
- Platinum: Catalyzes the oxidation of carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons, helping to convert these harmful substances into less toxic gases.
- Palladium: Assists in the oxidation of hydrocarbons and the reduction of nitrogen oxides, contributing to effective emissions control.
- Rhodium: Plays a critical role in reducing nitrogen oxides, ensuring that these gases are converted into less harmful substances.
Each type of catalyst:
- Has specific functions in the emissions reduction process.
- Works in conjunction with other catalysts to ensure comprehensive treatment of exhaust gases.
- Platinum, palladium, and rhodium are used as catalysts in catalytic converters.
- Each type has specific functions in emissions reduction.
- They work together to ensure effective treatment of exhaust gases.
What Are Catalytic Converters Good For?
Catalytic converters offer several benefits that impact both the environment and vehicle performance. They are designed to reduce the harmful effects of exhaust emissions, contribute to cleaner air, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. Their advantages extend beyond environmental benefits, affecting vehicle performance, fuel economy, and legal compliance.
Environmental Benefits
One of the primary benefits of catalytic converters is their impact on the environment:
- Reducing Pollution and Emissions: Catalytic converters help lower the levels of toxic gases such as carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides in vehicle emissions. This reduction in pollutants contributes to cleaner air and less environmental damage.
- Impact on Air Quality: By converting harmful gases into less harmful substances, catalytic converters improve air quality, which can have positive effects on public health and the environment.
These environmental benefits are crucial for addressing pollution and promoting a healthier planet.
- Catalytic converters reduce pollution and emissions.
- They contribute to improved air quality and environmental protection.
- These benefits are essential for public health and environmental sustainability.
Benefits to Vehicle Performance
Catalytic converters also offer advantages related to vehicle performance:
- Improving Engine Efficiency: By ensuring that exhaust gases are properly treated, catalytic converters help maintain optimal engine performance and efficiency.
- Enhancing Fuel Economy: Effective emissions control can lead to better fuel economy, as the engine operates more efficiently with reduced exhaust gases.
These performance benefits support the overall functionality and efficiency of the vehicle.
- Catalytic converters help improve engine efficiency and fuel economy.
- They ensure optimal performance by treating exhaust gases.
- These benefits enhance the overall functionality of the vehicle.
Legal and Regulatory Benefits
Catalytic converters play a crucial role in ensuring that vehicles comply with emissions regulations:
- Compliance with Emissions Standards: By reducing harmful emissions, catalytic converters help vehicles meet legal requirements for air quality and emissions control.
- Avoiding Fines and Penalties: Proper functioning of catalytic converters helps vehicle owners avoid fines and penalties associated with non-compliance with emissions regulations.
These legal and regulatory benefits are important for maintaining vehicle compliance and avoiding legal issues.
- Catalytic converters help vehicles comply with emissions standards.
- They assist in avoiding fines and penalties related to emissions.
- These benefits are crucial for regulatory compliance and legal adherence.
Conclusion About What’s the purpose of a catalytic converter?
In summary, catalytic converters are essential for reducing the environmental impact of vehicle emissions, improving air quality, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Their main purpose is to convert harmful exhaust gases into less harmful substances, contributing to cleaner air and better public health. Understanding the role of catalytic converters, the associated theory test, and the function of catalysts provides valuable insights into their importance in vehicle maintenance and environmental protection. Regular maintenance of catalytic converters is crucial for maintaining their effectiveness and ensuring that vehicles meet emissions standards. By appreciating the significance of catalytic converters and adhering to proper maintenance practices, vehicle owners can contribute to a healthier environment and enjoy the benefits of improved vehicle performance.
- Catalytic converters are vital for emissions reduction and regulatory compliance.
- Understanding their role helps in maintaining vehicles and protecting the environment.
- Proper maintenance ensures effectiveness and contributes to a healthier planet.
You Also Like It:
You’re driving a car fitted with automatic transmission. Why would you use kick-down?
Releated Posts
MAB Instructor Certification: Your Gateway to Professional Crisis Management Leadership
In today’s fast-evolving professional environments—especially in healthcare, mental health, education, and corrections—conflict and aggression can arise without warning.…
Freewayget.com: Your Ultimate Platform for Deals, Discounts, and Digital Products
Introduction to Freewayget.com In today’s fast-paced digital world, finding reliable platforms that offer authentic discounts, deals, and digital…
Affordable & Fast Embroidery Digitizing Services in Your Area
Embroidery digitizing services provide corporations, designers, and people with brilliant embroidery-equipped designs by means of changing art work…
Introduction to hdhub4u nit
In this article, we will delve into the details of hdhub4u nit, exploring its features, benefits, and why…